

(al-VEE-oh-ly) Tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles (tiny branches of air tubes in the lungs). Read More: What does basic fuchsin stain? What is alveolar sac? The main difference between the shunt and dead space is that shunt is the pathological condition in which the alveoli are perfused but not ventilated, whereas dead space is the physiological condition in which the alveoli are ventilated but not perfused. What is the difference between dead space and shunt? What is alveolar hypoventilation?Īlveolar hypoventilation is defined as insufficient ventilation leading to hypercapnia, which is an increase in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide as measured by arterial blood gas analysis (PaCO 2). Capillary shunting is defined as blood that goes from the right side of the heart to the left side of the heart via pulmonary capillaries that are adjacent to unventilated alveoli. What is anatomical shunt?Īnatomic shunting is defined as blood that goes from the right side to the left side of the heart without traversing pulmonary capillaries. For example, a surgeon may implant a tube to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain to the abdomen. (shunt) In medicine, a passage that is made to allow blood or other fluid to move from one part of the body to another. If a train is shunted, it’s diverted from the main track onto a side track. … Although shunt usually refers to a tube that drains blood or other fluid out of a part of the body, shunt also means to bypass. How do you fix a pulmonary shunt?Ī shunt is a small tube that goes inside the body to drain fluid. Examples include pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndroime. What is physiological shunt in lungs?Ī physiological shunt exists when nonventilated alveoli remain perfused, thus functioning as a shunt even though there is not an anatomic anomaly.
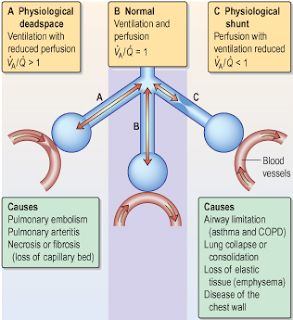
What causes pulmonary shunting?Ĭauses of shunt include pneumonia, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), alveolar collapse, and pulmonary arteriovenous communication. The deoxygenated blood (mixed venous blood) bypasses the ventilated alveoli and mixes with oxygenated blood that has flowed through the ventilated alveoli, consequently leading to a reduction in arterial blood content. Shunt is defined as the persistence of hypoxemia despite 100% oxygen inhalation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
